Circuit Symbols and Conventions
Circuits model electrical systems
- Voltage is work done per unit charge
- Potential difference- difference in electrical potential between two points in an electric field
- A force used to move charge between two points in space
- Moving charges produce an electric current
- Moving charges can do electrical work the same way moving objects do mechanical work
- Electrical energy is the capacity to do electrical work
- Electrical power is the rate at which work is done
Resistance
- Resistance is the opposition to the flow of current
- Ohm's Law:
- Resistance is also proportional to the Resistivity of the material
- and are the length and area of the conductor, respectively.
Sources and Nodes
Everything in a circuit can be modelled as either a source, or a node.
Voltage Sources
- DC and AC voltage sources
- DC source has positive and negative terminals
- Ideal voltage source has 0 internal resistance (infinite conductance)
- Supplies constant voltage regardless of load
- This is an assumption, is not the case in reality
Current Sources
- Ideal current source has infinite resistance (0 conductance)
- Supplies constant current regardless of load
- Also an assumption
- In reality, will have some internal resistance and therefore a maximum power limit
Dependant sources
- Diamond-shaped
- Sources depend on values in other parts of the circuit
- Model real sources more accurately
Nodes
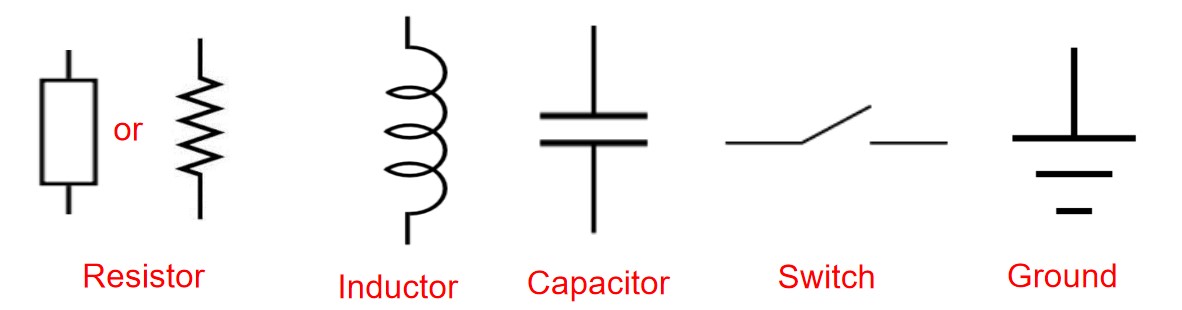
All passive elements: generate no electrical power.
- Resistors provide resistance/impedance in Ohms ()
- Inductors provide inductance in Henries ()
- Capacitors provide capacitance in Farads ()
The voltage rise across an impedance conducting current is in opposition to the flow of current in the impedance.
Basic Conventions
Electrical current always flows from high to low potential.
- If the direction of the current in a circuit is such that it leaves the positive terminal of a voltage source and enters the negative terminal, then the voltage is designated as negative
- If the direction of the current is such that it leaves the negative and enters the positive, then the voltage is positive
- The sign of the loop current is the terminal that it flows into
The power absorbed/produced by a source is .
- A voltage source is absorbing power if it is supplying a negative current
- A voltage source is producing power if it is supplying a positive current
The power dissapated in a resistor is .
Resistors in series and parallel
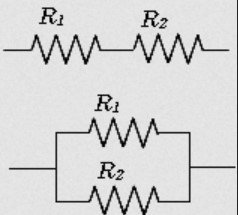
Resistors in series:
Resistors in parallel:
Resistors dissipate electrical power, so there is a drop in voltage accross them, in the direction of current flow. Therefore, the voltage rise is in opposition to the direction of current
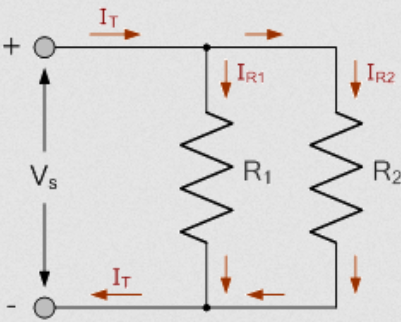
Voltage dividers
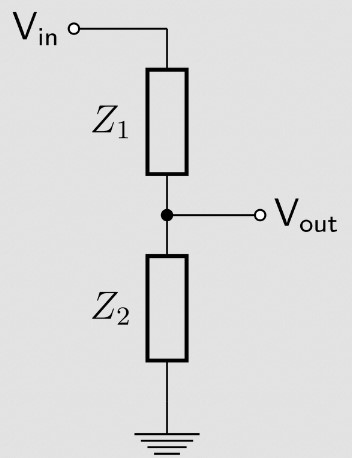
Using two resistors to divide a voltage
In the general case:
Current Dividers
Similar deal to voltage divider