Skip Lists
- When implementing sets, the idea is to be able to test for membership and update elements efficiently
- A sorted array or list is easy to search, but difficult to maintain in order
- Skip lists consists of multiple lists/sets
- The skip list
- contains all the elements, plus
- is a random subset of , for
- Each element of appears in with probability 0.5
- contains only

Search
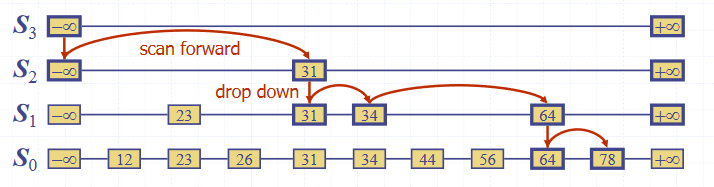
To search for an element in the list:
- Start in the first position of the top list
- At the current position , compare with the next element in the current list
- If , return
- If , move to the next element in the list
- "Scan forward"
- If , drop down to the element below
- "Drop down"
- If the end of the list () is reached, the element does not exist
Insertion
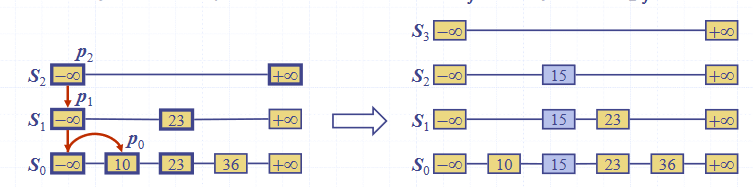
To insert an element into the list:
- Repeatedly toss a fair coin until tails comes up
- is the number of times the coin came up heads
- If , add to the skip list new lists
- Each containing only the two end keys
- Search for and find the positions of the items with the largest element in each list
- Same as the search algorithm
- For , insert k into list after position
Deletion
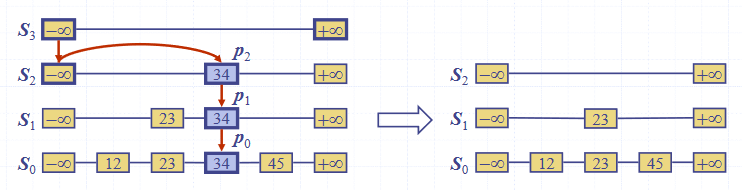
To remove an entry from a skip list:
- Search for in the skip list and find the positions of the items containing
- Remove those positions from the lists
- Remove a list if neccessary
Implementation
A skip list can be implemented using quad-nodes, where each node stores
- It's item/element
- A pointer to the node above
- A pointer to the node below
- A pointer to the next node
- A pointer to the previous node
Performance
- The space used by a skip list depends on the random number on each invocation of the insertion algorithm
- On average, the expected space usage of a skip list with items is
- The run time of the insertion is affected by the height of the skip list
- A skip list with items has average height
- The search time in a skip list is proportional to the number of steps taken
- The drop-down steps are bounded by the height of the list
- The scan-forward steps are bounded by the length of the list
- Both are
- Insertion and deletion are also both