Electrical Systems
Similar to mechanical systems, models of electrical systems can be constructed. Similar deal to ES191.
Variables
- Current in amps (A)
- Voltage in volts (V) -- not v for voltage, e is used in systems
- Power in watts
Elements
Capacitors
- Store electrical energy in a reversible form
- Capacitance measured in Farads (L)
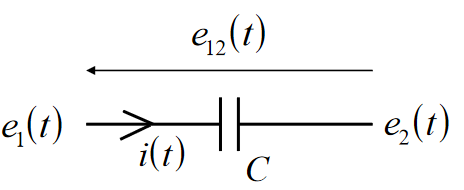
Elemental equation:
Energy stored:
Inductors
- Store magnetic energy in a reversible form
- Inductance measured in Henries (H)
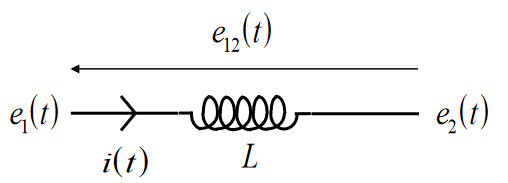
Elemental equation:
Energy Stored:
Resistors
- Dissapates energy
- Non-reversible
- Resistance measured in Ohms ()
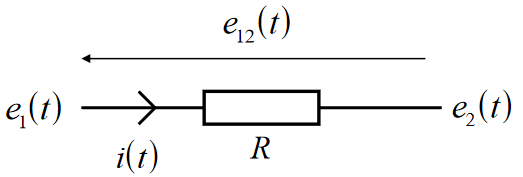
Elemental Equation (Ohm's law):
Voltage Source
- Provides an input of energy to the system.
- Input voltage
Kirchhoff's Laws
- Describe how elements interconnect and transfer energy between them
- KVL - voltages around a closed loop sum to zero
- KCL - currents about a node sum to zero
Example
Form a differential equation to model the following electrical system/circuit:
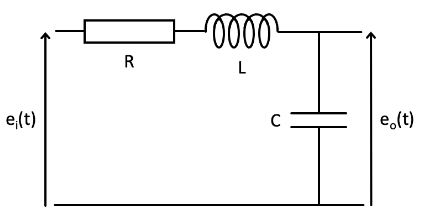
Elements:
- Resistor:
- Capacitor:
- Inductor:
KVL - the voltages round the loop sum to zero:
Using the capacitor equation, and the fact that :