Thermal Systems
- User to model heat transfer
- For example in a house
- Or in electronic components
- Determine efficiency of elements
- Determine thermal operating ranges for components
Variables
-
Rate of heat flow in watts ()
-
Temperature, in Kelvins (K)
-
Analogous to current and voltage in electrical systems
Elements
Thermal Capacitor
- Stores heat energy in a reversible way
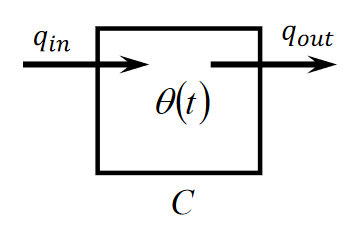
Elemental equation:
Where is the net heat flowing in, ie .
Thermal Resistor
- Dissapates heat
- Non-reversible
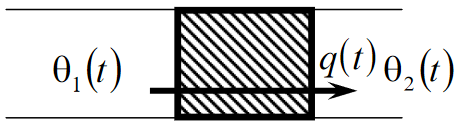
Any object that restricts heat flow when heat flows from on medium to another can be modelled as a resistor. Elemental equation:
Where is the flow of heat from the temperature on one side of the resistor to the temperature on the other.
Interconnection Laws
Compatibility Law:
- Temperatures are identical where elements touch,
Equilibrium Law:
- Elemental heat flow rates sum to zero at connection points
Examples
Develop a thermal model for someone doing winter sports. Assume:
- Ambient temperature
- Body temperature
- Thermal resistance between body and ambient (the person is wearing a coat)
- Heat generated by body
The rate of heat flow out is the difference in ambient and body temperature accross the resistor:
In the thermal capacitor, the net input heat is proportional to the rate of change of temperature:
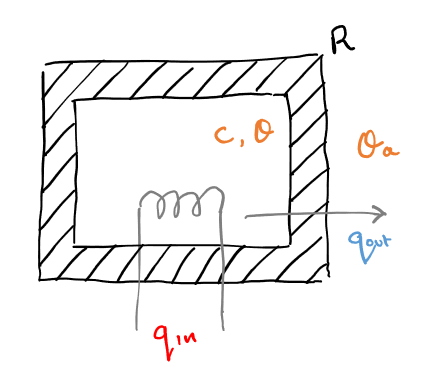
Combining the two equations gives: